

As we prepare to design IoT devices for large-scale networking, choosing the appropriate LTE IoT standard poses a challenge. But there is a problem that we need to solve from the beginning of product solution design, which affects what hardware our devices require and which operators will be used when the devices are released.
As 2G and 3G networks decline, existing large-scale cellular IoT devices will likely use one of the following 4G LTE standards: LTE Cat.1, LTE-M, or NB-IoT. When making a choice, we need to understand the differences between LTE Cat.1, LTE-M, and NB-IoT.
1.LTE Cat.1
Long Term Evolution (LTE) networks impose data size limits when data is transmitted over cellular networks. In 2008, standardization body 3GPP Release 8 defined five categories of user equipment (UE) specifications.
LTE Cat.1 defines a maximum data transfer rate of 5 Mbps upload (5 Mbps UL) and 10 Mbps download (10 Mbps DL).
Common application scenarios of LTE Cat 1 include: IoT retail applications, home security systems, smart wearable devices, smart watches, etc.
2. NB-IoT
Today, the IoT industry is looking for lower-cost chipsets and modules, and many IoT systems no longer require higher transmission rates. The Narrowband IoT (NB-IoT) standard is designed for IoT devices with lower data requirements. Data transfer rates are limited to approximately 160 kbps in 3GPP Release 14. If we do not need higher data transmission rates, we can choose NB-IoT to reduce the cost and power consumption of the product.
Common application scenarios of NB-IoT: smart agricultural applications, smart building applications, environmental pollution monitoring systems, industrial IoT sensors, etc.
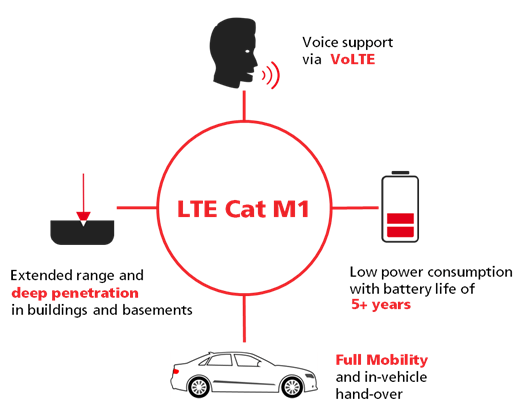
3.LTE-M
In terms of data transmission rate limits, the data transmission rate of LTE-M is between NB-IoT and Cat.1; the LTE-M data transmission rate is as high as 1.1 Mbps. In addition, both LTE-M and NB-IoT reduce the cost, power consumption and network capacity of large-scale IoT systems.
Cat.1 applies to all cellular networks in the world. If our products need to be marketed globally, Cat.1 is the best choice. If the data transmission data requirements of our products are between the data transmission rates of NB-IoT and Cat.1, then LTE-M has more advantages in large-scale IoT applications.
Common IoT application scenarios of LTE-M: smart cities, smart homes, smart healthcare, etc.
How do we choose NB-IoT, Cat.1, Cat.M?
First of all, we need different products. We need to choose based on product needs or project needs. NB-IoT, Cat.1, and Cat.M all have their own advantages.
1. Product performance
First of all, we need to determine the key requirements of our products. For example, whether our equipment has higher requirements for data transmission rate. If there are higher requirements, we need to choose Cat.1 with higher transmission rate to develop our products. At the same time, in terms of product performance, we also have requirements for power consumption, delay, and reliability. For example, our products are mobile products and are inconvenient for wiring and power supply installation, so we will use battery power supply, so when choosing We will give priority to low-power products and finally choose a protocol that suits us based on other needs.
2. Cost
Cost is important in any product and project and we need to choose according to our budget. When choosing LTE products, we must not only pay attention to our development costs and material costs, but also consider the costs we pay for operators. When our products are used for a long time, the operator fees will be higher.
3. Project cycle
The development difficulty, material supply cycle, and production testing difficulty of our products will all affect our choice.
Related article:
3 steps to learn the TCP/IP protocol of the communication protocol
How USB2.0 device establishes connection with the host
An overview of the matter protocol
HTTP VS.RPC, which protocol is the best







