

Crystal oscillator is an important electronic component, which is widely used in various electronic devices. According to its internal structure and working principle, crystal oscillator can be divided into two types: active crystal oscillator and passive crystal oscillator. The following are the main differences between active crystal oscillators and passive crystal oscillators:
Working principle:
Passive crystal oscillator: The English name is Crystals, which is the abbreviation of crystal resonator and is a resonant device based on quartz crystal. It is essentially a quartz crystal element, a piece of quartz crystal that has been cut and machined to a specific shape and size. When excited by an electric current, it generates a precise frequency using the natural electromechanical effect of the quartz crystal, which oscillates under the action of an electric field. The frequency range of our commonly used passive crystal oscillators is between a few kHz and tens of MHz, but specific applications may require higher or lower frequencies.

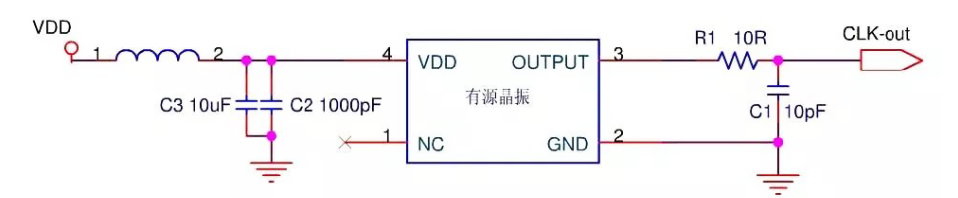
Active crystal oscillator: The English name is Crystal oscillator, which is the abbreviation of crystal oscillator. This is a crystal oscillator device integrated with an oscillator circuit, which can directly output a stable square wave signal. Its basic working principle is to use the piezoelectric effect of the quartz crystal and the feedback mechanism of the oscillator circuit. When the quartz crystal is subjected to external pressure, it generates a voltage, and then the oscillator circuit feeds back the voltage and increases it, thus maintaining the oscillation of the crystal.
Structure and Package:
Passive crystal oscillator: usually small and simple to package. Common package forms include HC-49U and so on.

Active crystal oscillator: Since the oscillator circuit is included inside and the internal structure is relatively complicated, the package of the active crystal oscillator is usually larger. Common package formats include SMD (Surface Mount Device) packages, which are suitable for modern PCB designs.
Output characteristics:
Passive crystal oscillator: The passive crystal oscillator itself does not directly output a square wave or sine wave signal, instead, it needs to be used in conjunction with an external circuit (such as a Pierce oscillator circuit) to generate an oscillating output. When combined with an appropriate circuit, a crystal oscillator will oscillate at its natural resonant frequency.
Active crystal oscillator: The main output of the active crystal oscillator is a square wave signal with stable and precise frequency and amplitude, and the frequency of the square wave signal is determined by the resonant frequency of the quartz crystal, usually in the range of several thousand Hz to tens of megahertz within range. The amplitude of the square wave signal is usually TTL or CMOS level.
Power requirements:
Passive crystal oscillator: no external power supply is required. The passive crystal oscillator itself does not require external power supply, but to generate oscillation, it usually needs to cooperate with an external oscillator circuit, and this circuit needs power supply.
Active crystal oscillator: An external power supply is required to drive the oscillator circuit. The active crystal oscillator is composed of a crystal and an internal amplifier circuit. This amplifier circuit needs to be driven by an external power supply to make the crystal produce stable oscillation.
Application fields:
Passive crystal oscillator: Due to its simplicity and low cost, it is widely used in various electronic products, such as watches, clocks, wireless communication equipment, computers, etc., as a frequency reference or clock source.

Active crystal oscillator: Because it can provide accurate and stable output frequency, it is often used in active crystal oscillators and is widely used in various electronic devices, especially applications that require a stable frequency reference. For example: communication equipment, computer, industrial control system, audio and video equipment, etc







