

Before explaining, we first need to understand what is the HTTP protocol and what is the RPC protocol.
What is the HTTP protocol
HTTP is a widely used network transmission protocol, which defines the communication format and communication method between the client (such as browser, mobile phone user APP, etc.) Based on a request-response communication model, that is, the server returns a response according to the request. Both the request and the response contain some information about the interaction between the two ends (client, server), such as methods and headers. , text, etc.
Related article :Where is HTTP3.0 stronger than HTTP2.0
HTTP has many advantages. It supports multiple data formats and encoding methods, and can realize cross-platform and cross-language communication. The communication is simple, flexible, and easy to expand. But at the same time it also has some disadvantages:
1) HTTP is stateless, and each request needs to re-establish the connection, which will increase network overhead and delay.
2) HTTP data transmission is based on text, which will result in a large amount of data and low parsing efficiency.
3) The security of HTTP is poor, and it is vulnerable to man-in-the-middle attacks and replay attacks.
4) The semantics of HTTP are weak, and it can only express basic addition, deletion, modification and query operations, and cannot satisfy complex business logic.
What is the RPC protocol
RPC, or Remote Procedure Call, is a remote procedure call protocol that allows a client to call a function on a remote server as if it were a local function.
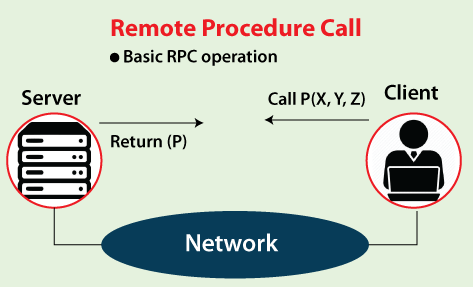
The advantages of RPC are efficient, powerful, and easy to use, but it also has some disadvantages, such as:
1) RPC is stateful and needs to maintain the connection state between the client and the server, which will increase the complexity and resource consumption of the system.
2) RPC data transmission is based on binary, which makes the data difficult to read and debug.
3) The compatibility of RPC is poor, and there may be inconsistencies in protocols and interfaces between different RPC frameworks.
4) The scalability of RPC is poor, and it is difficult to support functions such as dynamic service discovery and load balancing.
Summary
To sum up, in actual application, HTTP and RPC have their own advantages and disadvantages, and there is no absolute distinction between good and bad. Choose the appropriate protocol for different usage scenarios. for example:
1) In the microservice architecture, frequent internal calls are required between services, and RPC can provide higher performance and reliability.
2) In distributed computing, a large number of computing tasks need to be distributed to different nodes for execution, and RPC can implement a more flexible load balancing and fault tolerance mechanism.
3) In real-time communication, low-latency and high-concurrency data exchange needs to be realized, and RPC can support multiple transmission protocols and communication modes.
4) And if you need to achieve cross-platform and cross-language communication, or need to support multiple data formats and encoding methods, or need to use existing HTTP infrastructure and tools, you can choose the HTTP protocol.
Of course, this is not an absolutely fixed combination. You can also combine the two protocols to achieve a better network, for example:
1) We can encapsulate the RPC protocol on the HTTP protocol, so that the RPC request can be forwarded and processed through the HTTP proxy or gateway.
2) We can use the HTTP protocol as the transport layer on the RPC protocol, so that RPC requests can use the characteristics of HTTP to implement caching, compression, encryption and other functions.
So in general, the emergence of RPC is to deal with network scenarios that require performance that cannot be met by the HTTP protocol. They are not mutually exclusive, but can be selected and combined according to different scenarios and needs.







