

6G frequency band definition
The Ministry of Industry and Information Technology recently announced that the 6GHz frequency band will be launched globally for 5G and 6G systems. 6G radio waves provide faster transmission speed, lower delay time, solve connection and congestion problems, and have larger capacity to meet the needs of high-performance games, high-definition multi-person conferences, and watching 8K high-definition video. 6GHz refers to the frequency band of 5925-7125MHz, and the bandwidth spectrum resource is 1200MHz. Spectrum resources are of great significance to the development of wireless communication technology, which is the key to the digital transformation of the country. 6G, an important part of the intermediate frequency spectrum, has the advantage of being compatible with low frequency bands and high frequencies, and can promote the development of 5G at a lower cost.
6GHz promotes the comprehensive development of 5G
Compared with 5G, 6G is faster, but 6G is more expensive. 6G is currently in the status quo of research and development. According to research, the spectrum in the low, medium and high frequency bands can stimulate the full potential of 5G.
Why is 6GHz important?
Spectrum resources promote the development of radio communication technology. As far as IMT cellular communication is concerned, the spectrum extent map for the main applications is shown below:
Below 1000MHZ:
There are many frequency band resources, the working frequency is low, the wavelength is longer, and the coverage area is farther, but the bandwidth is narrow, which is not conducive to the development of large broadband services.
1000MHZ-7125MHZ:
Below 6Ghz, the main frequency band of mobile communication, can realize large broadband and large capacity transmission.
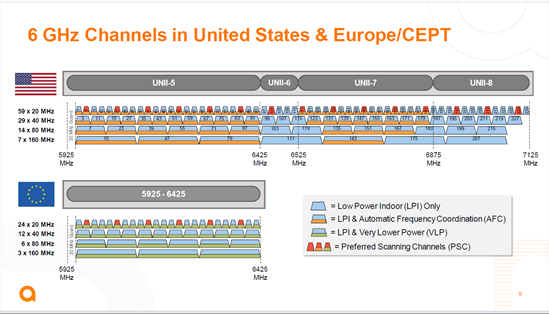
The traditional WI-FI frequency band refers to 2.4G and 5GHz. In order to meet the needs of larger capacity and lower latency, the 6Ghz era has ushered in. The spectrum diagram of 6Ghz is as follows:
Compared with 2.4G and 5G, 6G has wide bandwidth and many channels. As far as the commonly used 40M bandwidth is concerned, there are 29 channels for WI-FI devices to choose from; so what are the benefits of so many channels? Considering each node of the network as a whole, from electronic devices such as computers and mobile phones to routers and networks, if any node reaches a bottleneck, it will not be able to improve the performance of the entire network. WI-FI devices mainly use 20M/40M bandwidth, generally equipped with two antennas, and support MIMO mode. Under 40M bandwidth, the maximum theoretical rate can reach 344Mbps, and 80M bandwidth can reach 700mbps. It can be seen that increasing channel resources can increase the rate. Although MIMO can increase the rate through multiple channels, it will increase the channel of the transmitter, resulting in higher power consumption of WI-FI.
6GHz Status
At present, terminals and network equipment supporting 6G have a place in the market. At the point of 6GHz, the attitude of the Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of my country has always been to support the allocation of 6GHz to 5G and future 6G use. Although 5G signals are not widely popularized, 6G technology is just around the corner. It is believed that 6G will be an outlet for wireless communications in the future.







