Low-power wireless communication can be realized through Bluetooth protocol and Bluetooth module.
The Bluetooth protocol is a standard protocol for wireless communication that enables data transmission and communication between devices within a short distance. The Bluetooth protocol focuses on simplicity, low power consumption, and cost-effectiveness, and is designed to meet a wide range of application needs. It provides reliable connectivity and efficient data transmission for various devices and scenarios.
The Bluetooth module is a hardware device integrated with the Bluetooth communication function, which can be easily embedded in various electronic devices. The Bluetooth module provides the implementation of the Bluetooth protocol and has the ability to communicate wirelessly with other devices. It usually includes a radio frequency chip, a baseband processor and related peripheral circuits, providing the device with the functions required for Bluetooth communication.
Content Express here
Origin of "Bluetooth"
The
origin of Bluetooth technology can be traced back to the early 1990s,
when Ericsson, a Swedish communication company, was trying to find a
wireless communication technology for simple wireless connection between
devices. Their goal is to create a standard that enables short-range
communication with low power consumption, allowing various devices to
communicate with each other and share data.
In 1994, Jim Kardach,
an engineer at Ericsson, and his team began developing the new
technology. Their research results were officially released in 1998 and
named "Bluetooth" to commemorate the medieval Danish king Harald Blåtand
(Harald Bluetooth), who unified Denmark and Norway in the 10th century,
symbolizing the meaning of unity and interconnection.
Bluetooth
technology was originally designed to replace traditional serial data
lines, such as connecting a computer to a printer, or connecting a
mobile phone to a headset. Its goal is to provide a simple, low-power,
affordable wireless communication solution that enables data transfer
between devices over short distances.
Bluetooth technology has
evolved and improved over time, including adding higher data transfer
rates, longer range, and support for different types of device
connections. Today, Bluetooth has become a common standard widely used
in wireless communication between various devices, such as mobile
phones, tablets, audio equipment, smart home devices, etc.
| Bluetooth Versions | Features and Specifications |
| Bluetooth v1.0 to v1.08 | Mandatory Bluetooth hardware device and address |
| Bluetooth v1.1 | IEEE standard 802.15.1-2002 |
| Bluetooth v1.2 | Faster connection |
| Bluetooth v2.0+EDR | Enhanced data rate |
| Bluetooth v2.1 | Secure simple pairing |
| Bluetooth v3.0 | High-speed data transfer |
| Bluetooth v4.0 | Low energy consumption; recently in use in apple i- phone 4s |
| Bluetooth v4.1 | Incremental software update |
| Bluetooth v4.2 | New feature for Internet of Things (IoT) |
| Bluetooth v5 | Increased speed for Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) |
| Bluetooth v5.1 | New feature in Core Specification Addendum (CSA) 6 |
| Bluetooth v5.2 | New features for LE |
Overview of Bluetooth Protocol
Introduction of Bluetooth protocol
The Bluetooth protocol is a wireless communication protocol for data transmission and communication between devices within a short distance. It uses low-power radio frequency technology and is capable of wireless communication on the 2.4 GHz frequency band. The main focus of the Bluetooth protocol is simplicity, low power consumption and cost-effectiveness to meet the needs of a wide range of applications.
Related article :
 Bluetooth
protocol features: Signals can be transmitted through walls and
briefcases. Up to eight devices can be connected in a piconet. Since the
device is omnidirectional, there is no need to aim your device.
Bluetooth needs to be regulated by the government because it is possible
to use the same standard
Bluetooth
protocol features: Signals can be transmitted through walls and
briefcases. Up to eight devices can be connected in a piconet. Since the
device is omnidirectional, there is no need to aim your device.
Bluetooth needs to be regulated by the government because it is possible
to use the same standard
Refer article : The evolution of bluetooth wireless communication technology
Wireless Technology Choice for the Smart Home: Bluetooth or WiFi?
Bluetooth protocol stack
Bluetooth
protocol stack: The Bluetooth protocol stack refers to a series of
software layers used to manage the communication between Bluetooth
devices. The Bluetooth protocol stack usually includes the following
layers:
Physical Layer: Handles the physical transmission of
wireless communications, including modulation and demodulation of radio
frequency signals, frequency hopping, etc.
Baseband Layer
(Baseband Layer): manages data transmission and error detection, and
handles the assembly and analysis of data frames.
Link Layer
(Link Layer): Responsible for establishing and managing connections
between Bluetooth devices, performing security operations such as
authentication and encryption between devices.
L2CAP layer
(Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol): Provides a logical
channel between the upper-layer application and the underlying link
layer, and supports data segmentation and reassembly.
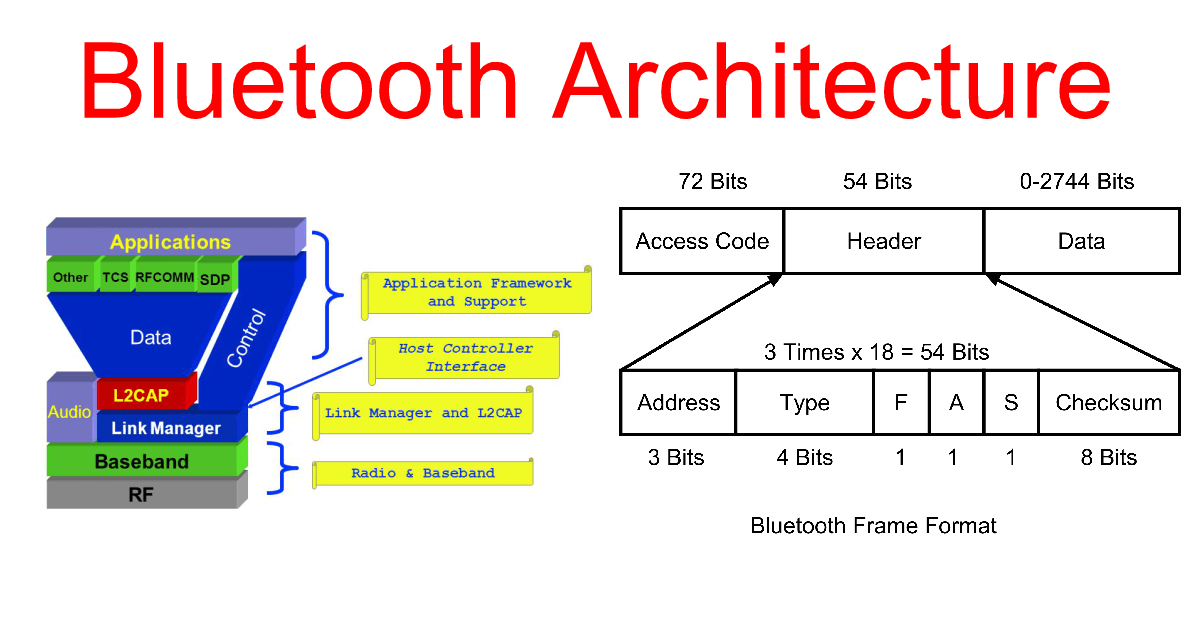
RFCOMM
layer (Radio Frequency Communication): Provides data transmission
services similar to serial ports, allowing applications to communicate
via Bluetooth.
SDP layer (Service Discovery Protocol): Used for
service discovery and information exchange between devices, enabling
devices to understand each other's functions and services.
Application
Layer (Application Layer): includes various applications and services,
such as file transfer, audio transfer, phone control, etc.
The protocol stack is the main function of Bluetooth, which allows Bluetooth to run and surpass other applications.
Core
Protocols: Includes Bluetooth radio, baseband, Link Manager Protocol
(LMP), Logical Link Control and Adaptation Protocol (L2CAP), and Service
Discovery Protocol (SDP). (standard)
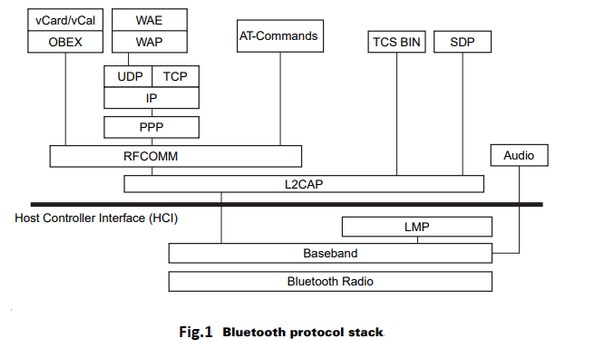
Protocols used: including
Point-to-Point Protocol (PPP), Internet Protocol (IP), User Datagram
Protocol (UDP), Transmission Control Protocol (TCP) and Wireless
Application Protocol (WAP). (taken from standard model)
Terminology Explanation:Introduction to UDP and TCP
Cable Replacement Protocol: It includes the Radio Frequency Communication (RFComm) protocol. It is an acronym for Radio Front End Components. (WAP serial interface is also provided)
Bluetooth master-slave relationship
In
Bluetooth communication, a master-slave (Master-Slave) relationship is
established between devices, which defines the roles and
responsibilities of devices in the communication process.
Master
device (Master): The master device is the controller in Bluetooth
communication, which is responsible for initiating and managing the
connection. The master device is usually a device with more processing
power and more complex functions, such as a mobile phone, computer, or
tablet. The master device plays an active role when initiating a
connection, controlling the timing and parameter settings of the
communication.
Slave device (Slave): The slave device is the
passive side, it accepts the connection request from the master device
and follows the instructions of the master device. Slave devices are
usually relatively simple devices such as Bluetooth headsets, smart home
devices, or sensors. The slave device passively responds to the
instructions of the master device in the communication, performs
corresponding operations or provides data.
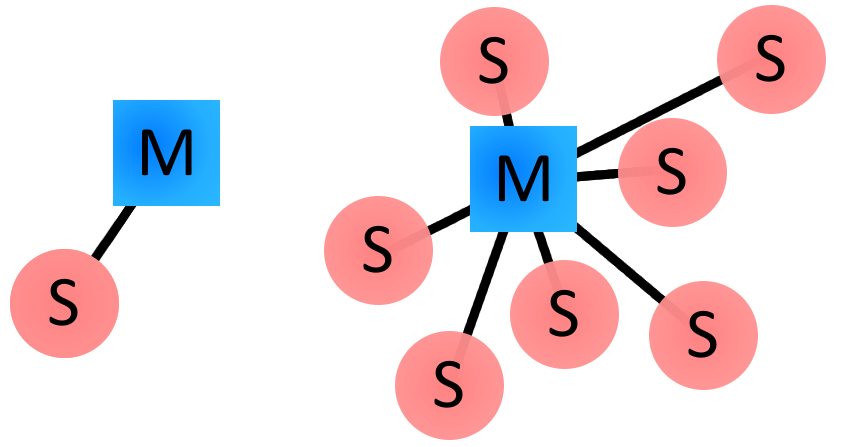
In the Bluetooth
communication process, a master device can connect multiple slave
devices at the same time to form a so-called Bluetooth network. The
master device can establish an independent connection with each slave
device, and perform data transmission and interaction with them. A slave
device can only establish a connection with one master device, but it
can communicate with other master devices by switching the connection of
the master device.
The determination of the master-slave
relationship is carried out during the connection establishment phase.
When the master device establishes a connection with the slave device,
they will negotiate to determine their respective roles. The roles of
the master device and the slave device can be switched during the
connection process so that the device can flexibly change its
communication role as needed.
Application of Bluetooth module
Bluetooth
module is a hardware device integrated with Bluetooth communication
function, which can be easily embedded in various electronic devices to
realize wireless communication and connection.
Common Bluetooth module application scenarios:
Bluetooth
Headphones/Speakers: A Bluetooth module is built into a headset or
speaker, allowing it to connect wirelessly to a phone, computer, or
other audio source device. Users can enjoy a wireless audio experience
through Bluetooth headphones or speakers.
Bluetooth
keyboard/mouse: The Bluetooth module is embedded in the keyboard or
mouse to achieve wireless connection with computers or other devices.
Users can conveniently control the device via a Bluetooth keyboard and
mouse, eliminating the limitations of wired connections.
Bluetooth
sensor: The Bluetooth module can be integrated with various sensors,
such as temperature sensor, humidity sensor, motion sensor, etc. By
connecting with Bluetooth, the sensor can transmit data to mobile phones
or other devices to realize real-time monitoring and data collection.
Smart
home devices: Bluetooth modules are used in smart home devices, such as
smart light bulbs, smart sockets, smart door locks, etc. Through
Bluetooth connection, users can remotely control and manage smart home
devices through mobile phones or other control devices.
Medical
equipment: Bluetooth modules can be embedded in medical equipment, such
as blood pressure monitors, blood glucose meters, heart rate monitors,
etc. These devices can be connected to mobile phones or other monitoring
devices via Bluetooth to transmit data to doctors or users for remote
monitoring and management.
Car equipment: Bluetooth modules are
widely used in car equipment, such as car audio systems, car phone
systems, and vehicle diagnostic equipment. It can wirelessly connect the
internal equipment of the vehicle with the mobile phone or other
external equipment to realize audio transmission, call function and
vehicle data monitoring.
Wireless transmission equipment:
Bluetooth modules can be used for wireless transmission equipment, such
as Bluetooth printers, Bluetooth scanners, Bluetooth barcode guns, etc.
These devices can be connected with computers or mobile devices via
Bluetooth for wireless data transmission and interaction.
Low Energy Bluetooth (LE Bluetooth) is a variant of Bluetooth technology designed to meet the needs for low power consumption and simple connectivity. It is also known as Bluetooth Low Energy (BLE) or Bluetooth Smart.

Bluetooth Low Energy is designed to optimize
traditional Bluetooth technology for longer battery life on
battery-operated devices. Compared with traditional Bluetooth, Bluetooth
Low Energy has the following characteristics:
Low Power
Consumption: Bluetooth Low Energy is designed to operate in a
power-saving mode, allowing devices to last longer. It employs a series
of optimization strategies, including fast connection establishment, low
power standby and short data transfer time, to reduce energy
consumption.
Simplified connection: Bluetooth low energy
uses a fast connection establishment mechanism to make the connection
process between devices easier and faster. It establishes a connection
within milliseconds, allowing for fast boot and data transfer.
Short-range communication: The communication distance of Bluetooth low
energy is usually shorter than that of traditional Bluetooth, generally
within a few meters. This helps reduce power consumption and provides
greater security because the communication range between devices is
narrower.
Data transfer rate: The data transfer rate of
Bluetooth Low Energy is relatively low, usually under 1 Mbps. This is
sufficient for transferring small amounts of data, such as sensor data
or simple control commands.
The application of Bluetooth Low Energy is very extensive, including but not limited to the following fields:
Internet of Things (IoT) devices: Bluetooth Low Energy can be used to
connect and control a variety of IoT devices such as smart home devices,
health monitoring devices, smart wearables, and more.
Fitness and sports equipment: Bluetooth low energy is widely used in
fitness trackers, heart rate monitors, motion sensors and other
equipment to realize wireless data synchronization and tracking with
mobile phones or computers.
Medical equipment: Bluetooth low
energy consumption is used to connect medical equipment, such as blood
pressure monitors, blood glucose meters, medical sensors, etc., to
achieve real-time data monitoring and remote data transmission.
Smart wearable devices: Bluetooth Low Energy can be used to connect
smart watches, smart glasses and other wearable devices to realize
interconnection and data interaction with mobile phones.
Indoor positioning and navigation: Bluetooth low energy can be used in
indoor positioning systems to provide real-time location tracking and
navigation services.
Ebyte Low Energy Bluetooth Module Recommended
Ebyte
is a supplier focusing on wireless communication modules. Its low-power
Bluetooth modules have excellent performance and reliability in the
field of wireless communication transmission. These modules feature
advanced Bluetooth Low Energy technology and are designed to meet the
needs of a wide range of IoT and connectivity applications.

Ebyte
low-energy Bluetooth module is famous for its highly integrated design.
They feature advanced RF technology and optimized power management for
excellent power efficiency. This enables the module to achieve long
battery life in battery-operated devices and extend the life of the
device.
These Bluetooth low-energy modules also provide a rich
set of interfaces and features that allow developers to easily integrate
the modules into their designs. The module has a flexible software
development environment and rich development tools to support fast and
reliable application development. In addition, the Ebyte low-power
Bluetooth module is compatible with mainstream development platforms and
operating systems, providing developers with more flexibility and
convenience.
- Low-power wireless communication-Bluetooth protocol and Bluetooth module
- The evolution of bluetooth wireless communication technology
- Application of Bluetooth Beacon in Warehouse Management
- Bluetooth BLE module as one of the mainstream way of wireless communication
- BLE5.0 Bluetooth module, master-slave integration, low power consumption!