The four stages of IoT communication are the perception layer, transport layer, network layer, and application layer. In each stage, different wireless technologies can be used to transfer information.
Article Outline:
The importance of the data transport layer
The
four stages of IoT communication are the perception layer, transport
layer, network layer, and application layer. The generation of these
stages involves the construction of the IoT system and the realization
of the components.
Perception layer: The perception layer is the
lowest layer in the Internet of Things, responsible for sensing and
collecting data in the environment. The perception layer is the bottom
layer of the Internet of Things, responsible for sensing and collecting
data in the environment. It includes various sensors, devices, and IoT
nodes that can sense and acquire various data in the environment, such
as temperature, humidity, light, motion, etc. The generation of the
perception layer involves the development, manufacture, and deployment
of sensors and devices and their connection to IoT systems. Commonly
used wireless technologies at this stage include:
Wi-Fi (Wireless Local Area Network): Suitable for indoor environments, providing high-speed data transmission and wide coverage.
Bluetooth: Suitable for short-range communication, often used to connect smartphones, sensors, and low-power devices.
ZigBee:
suitable for sensor networks with low power consumption and low data
rate, often used in scenarios such as home automation and industrial
control.
RFID (Radio Frequency Identification): Used to track and
identify tags or objects in real-time, often used in logistics and
supply chain management.
Refer article : Application of RFID Technology in Intelligent Logistics
Transport layer: The transport layer
is responsible for transmitting the data collected by the perception
layer to the network layer for processing. The transport layer is
responsible for transmitting the data collected by the perception layer
to the network layer for processing. This stage, it involves the
selection and implementation of wireless communication technology and
network protocol. According to the specific application requirements of
the Internet of Things, select the appropriate wireless technology, such
as Wi-Fi, Bluetooth, ZigBee, cellular network, etc. At the same time,
it is also necessary to determine the communication protocol and data
format of the transport layer to ensure reliable transmission and
correct analysis of data. Commonly used wireless technologies at this
stage include:
Wi-Fi: Provides high-speed data transmission and wide coverage, suitable for transmitting data within a local area network.
Cellular
networks (e.g. 4G, 5G): Provide wide area network coverage, suitable
for long-distance communication and Internet connectivity.
Related article :
The IOT Connectivity Puzzle: Cellular vs. Non-Cellular
Cellular and Industrial IoT: Simple, Scalable and Secure Connectivity
LPWAN (Low Power Wide Area Network): such as LoRaWAN, NB-IoT, etc.,
suitable for long-distance communication of low-power devices.
Network
layer: The network layer is responsible for establishing connections
and routing data in IoT. At this stage, the network infrastructure of
the Internet of Things needs to be established, including network
architecture, routers, gateways, and servers. The generation of the
network layer involves the configuration and deployment of network
equipment, as well as the implementation and management of network
protocols. At the same time, it is also necessary to consider the
requirements of network security and data privacy protection. Commonly
used wireless technologies at this stage include:
IP (Internet Protocol): IoT devices can use IP for communication and internet connection.
6LoWPAN
(IPv6 over Low-Power Wireless Personal Area Networks): Adapts the IPv6
protocol to a low-power wireless network to realize the interconnection
of IoT devices.
MQTT (Message Queuing Telemetry Transport): A lightweight messaging protocol used to deliver messages on the Internet of Things.
Related Article
Application
layer: The application layer is the uppermost stage in IoT and is
responsible for processing and applying data. IoT applications and
services need to be developed and deployed. According to specific
application requirements, develop corresponding application software and
algorithms to realize data processing, analysis, and application. The
generation of the application layer involves software development, data
analysis, and customization of application scenarios to meet the needs
of different fields and industries. Commonly used wireless technologies
at this stage include:
HTTP (Hypertext Transfer Protocol): Used to transfer data between web applications and cloud services.
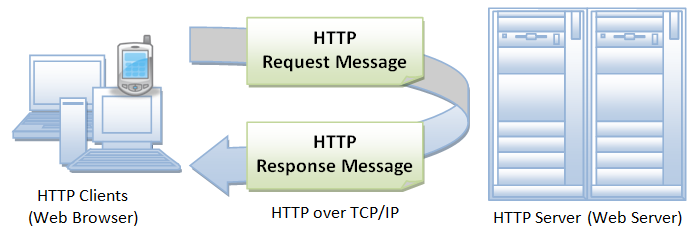
CoAP (Constrained Application Protocol): a lightweight application layer protocol
The importance of the data transport layer
The
data transmission layer is of great significance in the entire
communication stage of the Internet of Things. It is responsible for
transmitting the data collected by the perception layer to the network
layer for processing. The following are the significance of the data
transport layer:
Data transfer: Data transfer is one of the core
functions of IoT. After the data is collected from the perception layer,
it needs to be transmitted to the network layer through the data
transmission layer for processing and analysis. The data transmission
layer ensures the reliable transmission of data for subsequent data
processing and application.
Data Connections: The data transport
layer establishes and maintains connections between IoT devices. It
provides communication channels that enable sensors and devices in the
perception layer to communicate with servers and cloud platforms in the
network layer. Through the data transmission layer, IoT devices can
exchange data and communicate with each other.
 Communication
: The data transmission layer implements the communication
protocol, which defines the rules and methods of data transmission.
Communication protocols include data format, transmission protocol, data
compression, encryption, etc., to ensure the integrity, security, and
validity of data during transmission. A suitable communication protocol
can improve the efficiency and reliability of data transmission.
Communication
: The data transmission layer implements the communication
protocol, which defines the rules and methods of data transmission.
Communication protocols include data format, transmission protocol, data
compression, encryption, etc., to ensure the integrity, security, and
validity of data during transmission. A suitable communication protocol
can improve the efficiency and reliability of data transmission.
Data
security: The data transmission layer plays a key security role in IoT
communication. By using techniques such as encryption and
authentication, the data transport layer protects the transmitted data
from unauthorized access and tampering. It ensures the confidentiality
and integrity of data during transmission, preventing data leakage and
attacks.
Data quality and real-time: The data transmission layer
plays an important role in the transmission speed and quality of data.
It ensures that data can be transmitted in real-time or near real-time,
meeting the timeliness requirements of IoT applications for data. The
data transmission layer is also responsible for monitoring errors and
losses during data transmission and correcting and retransmitting to
ensure the accuracy and integrity of data.
FREE TRIAL AT CDEBYTE :
Explore Our Free trial and Evaluate More Discounts
 |
- Introducing 11 Common IoT Wireless Communication Protocols: How to Choose the Best Protocol
- 4 Technologies Learn How LPWAN Enables Communication Between IoT Devices
- How USB2.0 device establishes connection with the host
- Modem & DTU sale |More price down|MAX 20% OFF
- Introducing LoRa stable diffusion: based on LoRa communication